
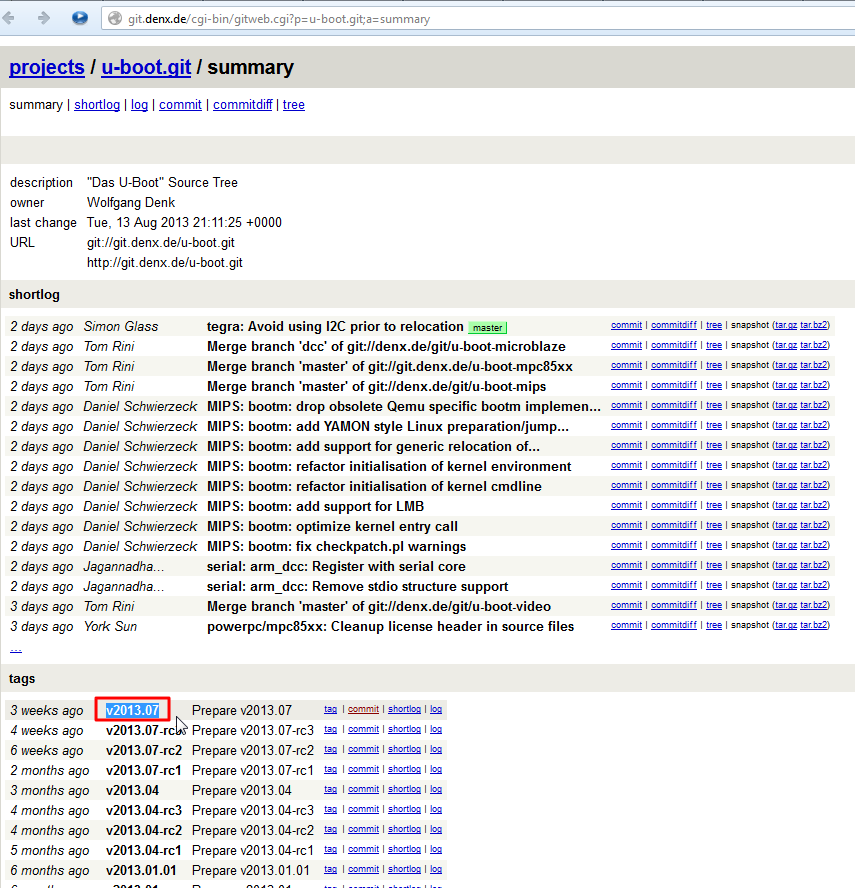
They can additionally verify the tag using git tag -v TAG_NAME. Anyone who runs git show TAG_NAME on the tag will also see your public key signature along with the tag information. If you are working on a major project and want to show without any doubt that you have worked on the release, you can sign it using your GPG private key as git tag -s TAG_NAME -m 'MESSAGE'. If you want your tags to be used by other contributors too, you need to push them using git push origin TAG_NAME The tag created is not pushed to remote automatically. Similarly, delete a tag using git tag -d TAG_NAME Then, create tag using git tag -a TAG_NAME -m 'MESSAGE' COMMIT_HASH If you want to create tag say 5 commits before HEAD, you can use git log to get the correct commit hash e.g git log -pretty=oneline -10 which shows the last 10 commits on the current branch. You do not always have to be at the HEAD or in the tip of the branch to create a tag. The tag information can be viewed without having to checkout the tag using git show TAG_NAME.

You can add more information using git tag -a TAG_NAME -m 'MESSAGE'
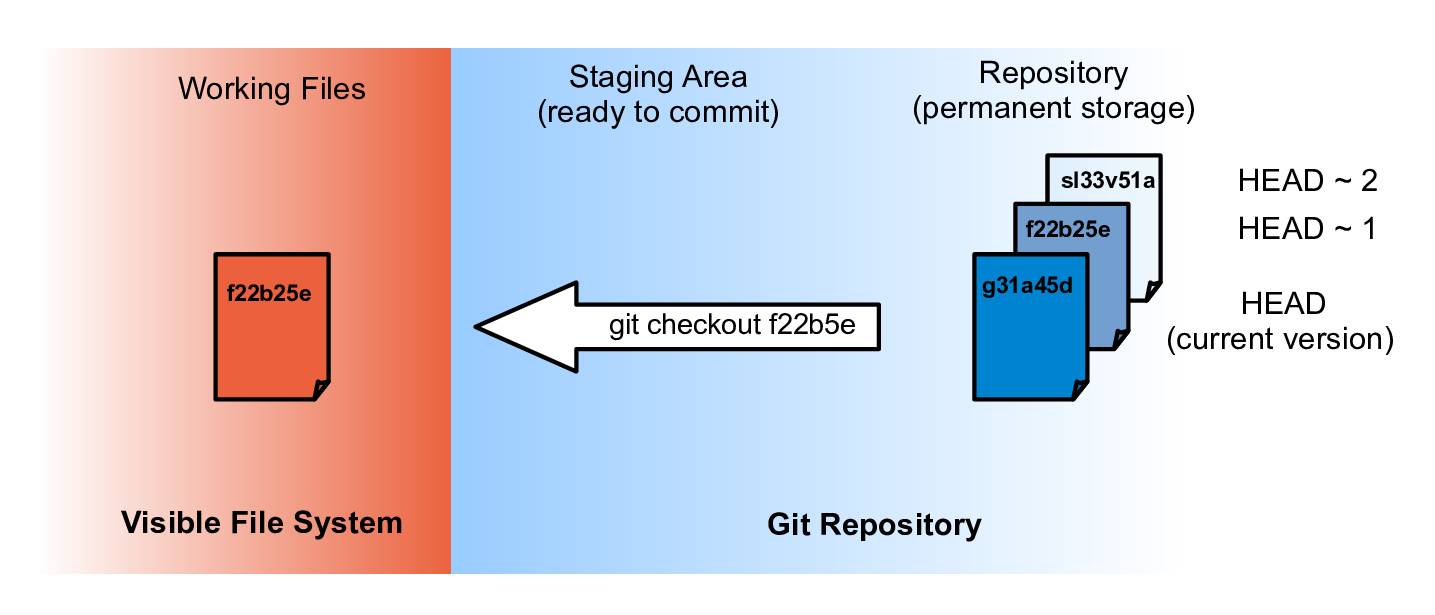
Do not worry, all it means is that you need to create a new branch if you want to retain any changes you make after checking out the tag.Ĭreate a new branch exactly at the commit of the tag using git checkout -b BRANCH_NAME TAG_NAME When you checkout the tag, git tells you that you are in "detached HEAD" state. The tag is linked to the specific commit and not to a branch. Anytime you want to reproduce bugs encountered on that version, simply do git checkout v1.0 and investigate. You can tag the commit as v1.0 using git tag v1.0. You just released a new version of your app. Tags are specific points in your code history which are useful to re-visit later e.g I think that tags are useful to know even when using the git cli.
#GIT CHECKOUT TAG FROM GITHUB HOW TO#
I read a post on dev.to which shows how to create git tags using GUI-based git clients.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
